Our Services
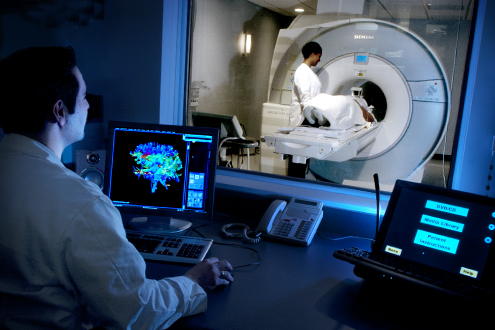
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI of the body uses a magnetic field which is powerful and a computer to product detailed pictures of the inside of your body. Even if you are pregnant or not, a body MRI can be perfectly tailored to diagnose and monitor treatment of various conditions in chest, pelvis and abdomen or can be used to monitor the baby in your body.
Scared of procedure..? Here is the snapshot !
The MRI examinations may be performed on outpatients or inpatients. Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or adjacent to the area of the body being studied. If a contrast material will be used in the MRI exam, a physician will insert an intravenous (IV) catheter also known as an IV line into a vein in your hand or arm. A saline solution may be used to inject the contrast material. The solution will drop through the IV to prevent blockage of the IV Catheter until the contrast material is injected. After the initial series of scans, additional series of images will be taken during or following the injection.
Want to know the Benefits Vs Risk of MRI?
Benefits
- MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation.
- MRI has proven valuable in diagnosing a broad range of conditions, including cancer, heart and vascular disease, and muscular and bone abnormalities.
- MRI enables the discovery of abnormalities that might be obscured by bone with other imaging methods.
- MRI allows physicians to assess the biliary system noninvasively and without contrast injection.
- The contrast material used in MRI exams is less likely to produce an allergic reaction than the iodine-based contrast materials used for conventional x-rays and CT scanning.
Risks
- The MRI examination poses almost no risk to the average patient when appropriate safety guidelines are followed.
- Although the strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI Exam
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is currently a recognized, but rare, complication of MRI believed to be caused by the injection of high doses of gadolinium-based contrast material in patients with very poor kidney function.
- There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast material is injected. Such reactions are usually mild and easily controlled by medication. If you experience allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance.
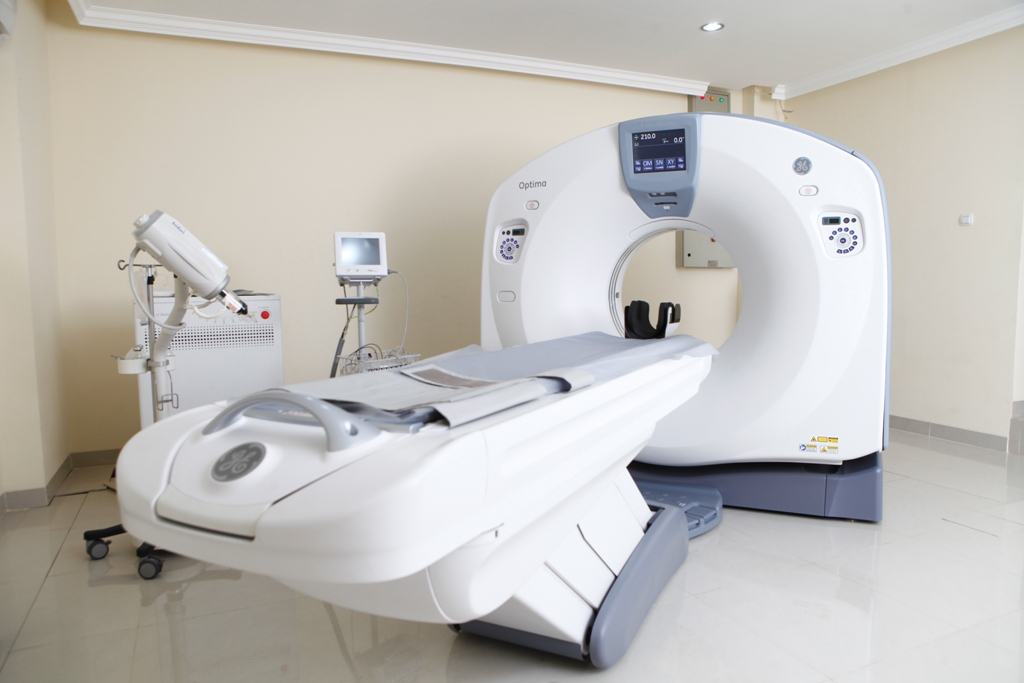
CT Scan
Computed Tomography of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless, noninvasive and accurate. Computed Tomography or more commonly known as CT or CAT scan, is a diagnostic medical test that, like traditional x-rays, produces multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body.
Scared of procedure..? Here is the snapshot !
Just like a normal scan, CT scan is similar with different body parts which absorb the x-rays in varying degrees. It is this crucial difference in absorption that allows the body parts to be distinguished from one another on an x-ray film or CT electronic image.
With CT scanning, numerous x-ray beams and a set of electronic x-ray detectors rotate around you, measuring the amount of radiation being absorbed throughout the body. Sometimes, the examination table will move during the scan, so that the x-ray beams follow a spiral path. A special computer program processes this large volume of data to create two-dimensional cross-sectional images of your body, which are then displayed on a monitor.
Want to know the Benefits Vs Risk of CT Scan?
Benefits
- A major benefit of CT is its ability to image bone, soft tissue and blood vessels all at the same time.
- CT scanning provides very detailed images of many types of tissue as well as the lungs, bones and blood vessels.
- CT Examination are fast and simple; in emergency cases, they can reveal internal injuries and bleeding quickly enough to help save lives.
- CT can be performed if you have an implanted medical device of any kind, unlike MRI.
Risks
- CT scanning is, in general not recommended for pregnant women unless medically necessary because of potential risk to the fetus in the womb.
- Women should always inform their physician and CT technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant.
- The risk of serious allergic reaction to contrast materials that contain iodine is extremely rare, and radiology departments are well-equipped to deal with them.
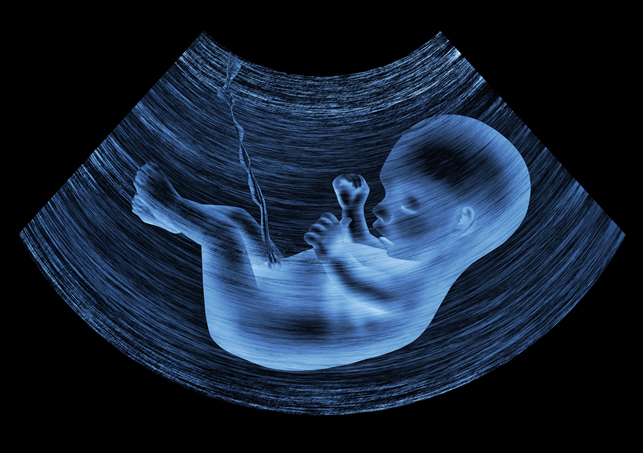
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of a baby within a pregnant woman, as well as the mother’s uterus and ovaries. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning involves the use of a small transducer and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sound that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation, thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient.
Scared of procedure..? Here is the snapshot !
After positioning the patient, the radiologist will apply a warm water-based gel to the area of the body being studied. The gel will help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The transducer is placed on the body and moved back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured.
Want to know the Benefits Vs Risk of Ultrasound?
Benefits
- Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive.
- An ultrasound exam may be temporarily uncomfortable, but it should not be painful.
- Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound allows the doctor to see inside the uterus and provides much information about the pregnancy.
Risks
- There aren’t any harmful effects on humans when it comes to diagnostic ultrasound.
Pathology
Pathology is a medical specialty that determines the cause and nature of diseases by examining and testing body tissues (from biopsies and pap smears) and bodily fluids (from samples including blood and urine). The results from these pathology tests help doctors diagnose and treat patients correctly. From then on we rely on blood tests, biopsies and a multitude of other pathology tests to prevent, diagnose and treat infections, allergies chronic diseases, cancers and countless other medical conditions.
How do Pathology Tests Work..?
Pathologists usually work in tandem with surgeons and play a critical role in the identification of the tissue removed during the process of a surgery – particularly in cases when there is a tumor suspected.
Pathologists are able to analyze a sample of tissue, whilst the surgery is still being conducted and advise the surgeon on the findings. This instant diagnosis is of great assistance to the surgeon as it helps in determining the next step in the surgical treatment of the patient. The tissue is analyzed over the next few days after the surgery in order to accurately diagnose the spread and the prognosis of the ailment.

Pathology Blood Tests
When it comes to pathology blood tests, the Complete blood count is one of the foremost medical practices and is very often considered to be the starting point for most medical investigations. The complete blood count takes into consideration the levels of all constituents of the blood- the red blood cells, the white blood cells and the platelets. Not only are the numbers counted but their proportions as well as overall hemoglobin levels are also measured in this test. The pathology test results are also used during a surgical procedure in order to help the surgeon make some decisions regarding the best method of operation. The tissue may also be analyzed and reanalyzed over the next few days as the medical team observes the changes in the body through the recovery process and ensure that everything is as it should be.
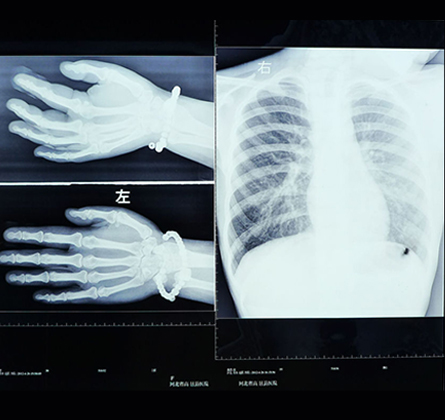
X-Ray
Bone X-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or joint dislocation. Bone x-rays are the fastest and easiest way for your doctor to view and assess bone fractures, injuries and joint abnormalities.
An x-ray is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Imaging with x-rays involves exposing a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body.
Scared of procedure..? Here is the snapshot !
The technologist positions the patient on the x-ray table and places the x-ray film holder or digital recording plate under the table in the area of the body being imaged. When necessary, sandbags, pillows or other positioning devices will be used to help you maintain the proper position.
You must hold very still and may be asked to keep from breathing for a few seconds while the x-ray picture is taken to reduce the possibility of a blurred image. The technologist will walk behind a wall to activate the x-ray machine. You may be repositioned for another view and the process is repeated. Two or three images will typically be taken.
Want to know the Benefits Vs Risk of X-Ray?
Benefits
- Bone x-rays are the fastest and easiest way for a physician to view and assess bone injuries, including fractures, and joint abnormalities, such as arthritis.
- X-ray equipment is relatively inexpensive and widely available in emergency rooms, physician offices, ambulatory care centers, nursing homes and other locations, making it convenient for both patient and physicians.
- Because x-ray imaging is fast and easy, it is particularly useful in emergency diagnosis and treatment.
- No radiation remains in a patient’s body after an x-ray examination.
Risks
- There is always a slight chance of cancer from excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk.
- The effective radiation dose for this procedure varies.
- Women should always inform their physicians or x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant.
Which Body Parts can be X-rayed?
While x-ray images are among the clearest, most detailed views of bone, they provide little information about muscles, tendons or joints.
Ultra Sonography
Ultrasound imaging of the pelvis uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures and organs in the lower abdomen and pelvis. Ultrasound is a safe and painless procedure and produce pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning, involving the use of a small transducer and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the proble through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image.
Scared of procedure..? Here is the snapshot !
After getting positioned on the table, the radiologist or sonographer will apply a warm water-based gel to the area of the body being studied. The gel will help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The transducer is placed on the body and moved back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured.

Want to know the Benefits Vs Risk of Sonography?
Benefits
- Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive.
- An ultrasound exam may be temporarily uncomfortable, but it should not be painful.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use and less expensive than other imaging methods.
- Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any ionizing radiation.
Risks
- For standard diagnostic ultrasound, there are no known harmful effects on human.
Copyright © 2024 All Rights Reserved by LOTUS IMAGING